Updated Wildfire Statistics[2024]
July 30, 2024
Joel Efosa
Joel efosa is an experienced NATIONWIDE fire damage real estate investor. As owner of fire cash buyer, my goal is to provide fire victims with more options wether its rehab, sell or financial help.
He’s been featured on multiple publications including
Realtor, Yahoo Finance, Business Insider, Nasdaq, MSN, Fox, Go Banking Rates, Homelight
At Fire Cash Buyer, we promote strict editorial integrity in each of our posts.
Wildfires are one of the most destructive events in nature and can burn several acres of land and structures.
Lightning and spontaneous combustion are common natural causes of wildfires. However, in most cases, fires are caused by human activity.
The continuous threat of wildfires affects our environment, society, and economy globally. Analyzing wildfire statistics is crucial to understanding its frequency, intensity, and impact.
This article will explore current trends, historical context, and future implications pertaining to wildfire data. A strong grasp of this issue is the first step to its prevention.
The Current State Of Wildfires in the United States
The United States has experienced a significant number of fires over recent years. As a result of climate change, prolonged droughts, and increased human activity in fire-prone areas, the frequency and intensity of wildland fires have increased.
This section covers the present-day landscape of wildfires, examining recent incidents and their impact on communities and ecosystems.
Recent Wildfire Statistics
Recent statistics highlight the alarming rise in wildfires, area and structures burned, and people displaced in recent years.
These data underscore the urgent need for comprehensive data analysis and strategic planning to address the underlying causes and mitigate the devastating effects of wildfires.
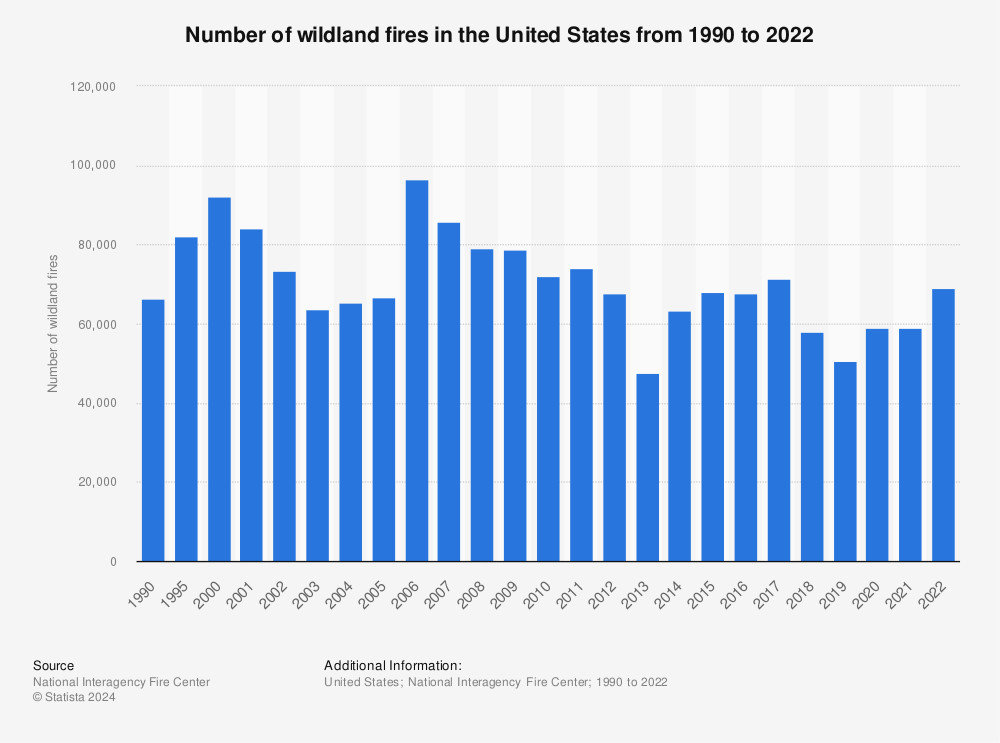
Number Of Wildfires In The Past Year
According to statistics provided by the National Interagency Fire Center (NIFC), the surge of wildland fires recorded by its database is likely attributed to a combination of factors.
These include extreme weather conditions and increased ignition sources.
This huge number of fires puts immense pressure on firefighting resources, public awareness campaigns, and preventive measures.
National Interagency Fire Center (NIFC) statistics show a total of 68,988 wildland fires recorded in the United States in the year 2022.
This total is a 17% increase compared to the number of wildfires in the United States in the previous year.
Of the total number of fires in 2022, 61,499, or 89% of these forest fires were caused by humans. Conversely, only 7,489, or 11%, were caused by lightning.
Among the 68,988 forest fires, 1,289, or 1.9%, were large wildfires.
A large wildland fire is defined differently depending on where it occurs.
- Eastern United States: Any fire with an area larger than 500 acres
- Western United States: Any fire that has consumed or covered an area greater than 1000 acres
Total Acreage Burned
Data defining the total area burned by wildfires can help illustrate the extent of the damage that disrupts local economies, wildlife habitats, and air quality.
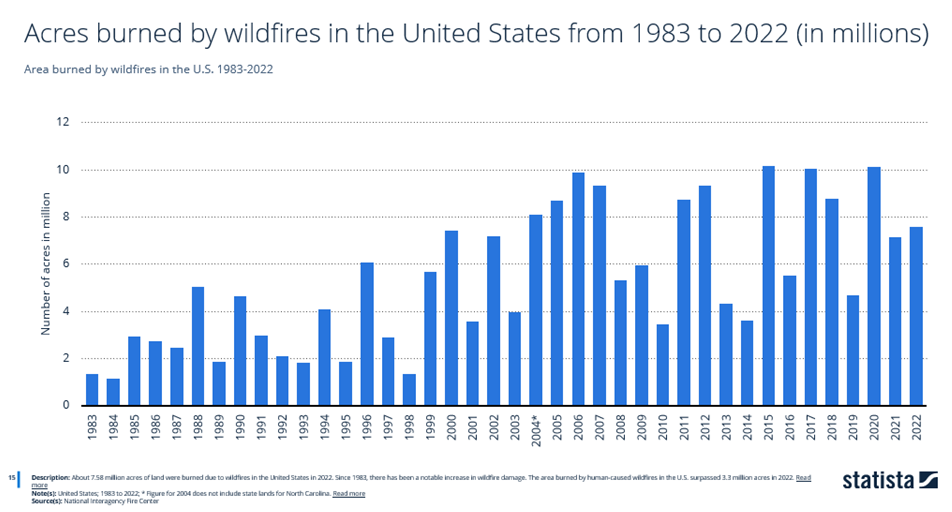
The above data from the National Interagency Fire Center (NIFC) shows that 7.58 million acres burned due to forest fires in the United States in 2022. Of this total area burned, 3.3 million acres were burned due to human activity.
The state of Alaska saw the largest area burned by wildfires across the United States in the same year, despite the state ranking 29th for total number of wildfires.
Alaska had 595 individual wildfires covering 3.1 million acreage burned. Alaska accounted for 41% of all acres burned due to wildland fires in the U.S.
Aside from Alaska, the database ranked New Mexico second in the area burned by wildfires with 859,906 acres. This is followed by Texas, Oregon, Idaho, Oklahoma, and California.
NOTE: The totals in the chart above include only reported wildfires, which can range in area from a few to millions of acres.
Comparison To Previous Years
There were only a total of 15 large fires recorded in 2022 globally, compared to the previous year's total of 19 large fires. This was the highest figure seen in the past decade.
However, the highest figure recorded was in 2000 with 30 large wildfires.
The database displays a slight decrease in large fires year-on-year.
Updated data from the National Centers for Environmental Information and NIFC found that forest fires in 2023 burned an average number of 2.6 million acres.
This is a marked reduction in acreage burned from 2022, which saw 7.5 million acres burned in total.
Despite this short-term reduction, the data from the last 20 years has shown an oscillating trend in the average number of acres burned per year.
Geographic Distribution Of Wildfires
As statistics prove, wildfires in the United States are not confined to a single region but are distributed across various geographic areas.
Certain states are particularly susceptible to wildfires due to their naturally dry climates or large dry portions. These include the following.
- Texas
- California
- North Carolina
- Georgia
- Oklahoma
- Alabama
- Oregon
Awareness of the distribution of wildfires per state is essential for efficient resource allocation and for developing targeted prevention and response plans.
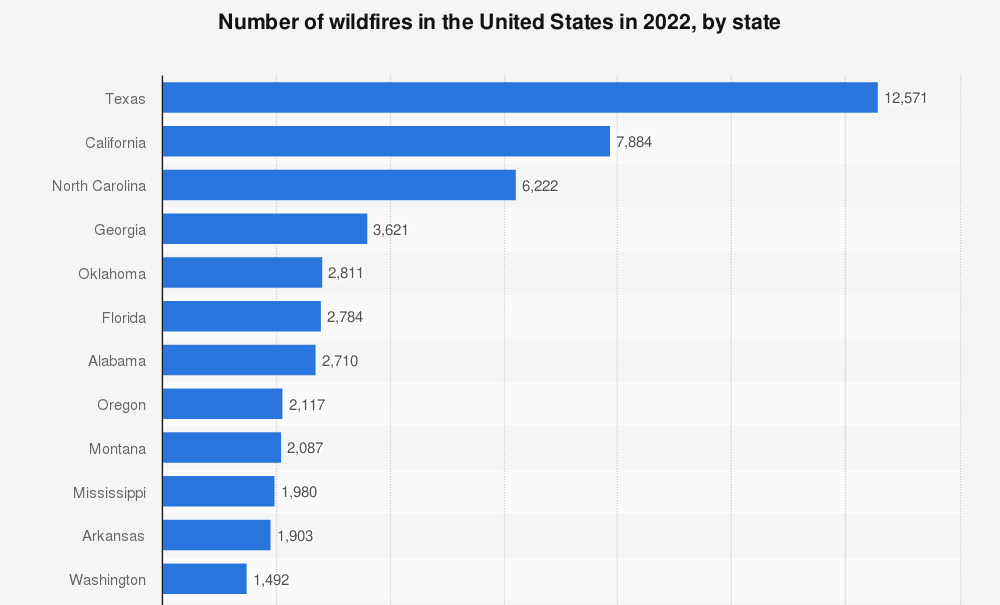
According to recent data shown on the graph, 5 States accounted for 48% of total wildfires in 2022, namely Texas, California, North Carolina, Georgia, and Oklahoma.
The state of Texas recorded over 12,500 individual wildfires in the same year. The high number of wildfires in the southern state resulted in nearly 672,000 acres burned.
California ranked second. A total number of 7,884 wildfires occurred throughout 2022.
Western states such as California, Oregon, Washington, and parts of Nevada and Arizona are prone to wildland fires due to their dry summers, strong winds, and extensive forests.
Seasonal Patterns And Trends
According to historical data provided by the National Interagency Fire Center, the wildfires with the largest number of acres burned occurred between 2004 and today.
The peak years were between 2015 and 2020. This trend coincided with these being the warmest years on record, according to the U.S. and Global Temperature indicators.
Data also found that the largest increases in area burned occurred during the spring and summer months. Drought, high temperatures, flammable vegetation, and strong winds contributed to these seasonal patterns.
Climate change is another trend that threatens to increase the acreage burned, frequency, and severity of fires.
Additionally, earlier spring melting and a reduction in available snowpack have led to a lack of available water. These conditions may lead to longer and more intense fire periods.
Causes And Contributing Factors
Wildfires can be caused by both human activities and natural occurrences, with each source presenting unique challenges for fire management.
Human-Caused Wildfires
As shown in relevant data, the majority of fires are caused by humans. These human activities range from accidental ignitions to deliberate acts of grazing or arson, all of which can have devastating consequences.
It is important to address these human-caused wildfires through the following initiatives.
- Public education
- Stricter regulations
- Increased enforcement
Percentage Of Human-Induced Fires
According to federal data and statistics cited by the National Park Service, 85-90% of wildfires in the United States occur due to human activities, making it the most common cause of wildland fires followed by lightning.
This high percentage should encourage proactive measures for fire prevention, like promoting responsible behavior and enhancing fire safety awareness in every state.
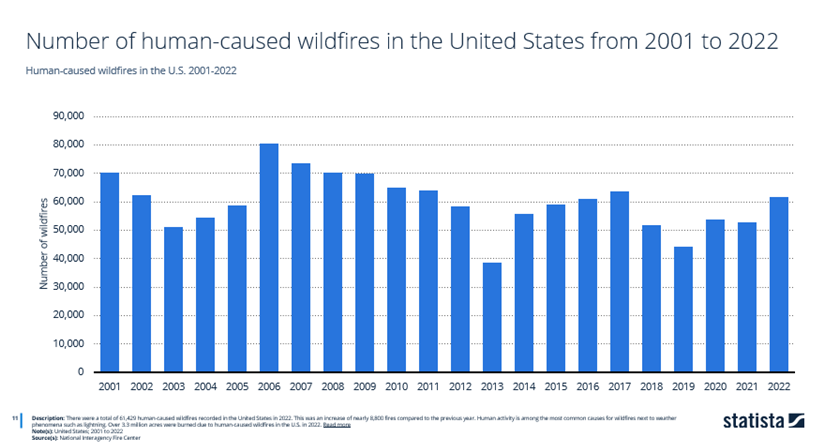
Updated data provided by the National Interagency Fire Center shows a recorded total of 61,429 wildfires caused by humans in the United States in 2022. This total represents a significant increase of nearly 8,800 fires compared to the previous year.
The 61,429 human-induced wildfires totals over 3.3 million acres burned.
Common Human Activities Leading To Wildfires
Here are several common activities by humans that can ignite forest fires.
- Arson
- According to data provided by the
National Fire Protection Association, a total of
52,260 intentional fires occurred between 2014 and 2018 in the U.S., resulting in an estimated 400 civilian deaths, 950 civilian injuries, and $815 million in direct property damage each year.
Motives for arson may include real estate speculation, building land reclamation, and pasture management.
- Unattended Campfires - A large number of fires occurred due to campfires that were not extinguished properly.
The Ham Lake fire in 2007 was one example of a forest fire caused by an unattended campfire. It burned down 75,000 acres of forest along the Gunflint Trail in the northern state of Minnesota.
- Burning Debris - Burning debris can easily lead to a forest fire. Wind can carry flames from a pile of burning yard waste to another area and start a new fire.
- Equipment Malfunction -
Research shows a number of forest fires were caused by faulty power lines in California in 2022. Furthermore, equipment malfunctions and sparks are the third most common cause of forest fires in the state. An average of 400 forest fires in California are ignited by these sparks per year.
According to California's database, The Zaca Fire (2007) is the fifth biggest forest fire on record and was caused by sparks from a metal grinder. The Carr Fire (2018) on the other hand, is the seventh most destructive California forest fire, caused by sparks from a trailer's broken wheel rim.
- Discarded Cigarette Butts - Lit cigarettes can ignite a wildland fire when they land on dry vegetation. Data in 2017 shows $6 billion was lost in property damage due to forest fires caused by discarded cigarettes.
Natural Causes Of Wildfires
The following are common natural ignition sources for forest fires.
- Lightning Strikes - Lightning is the most common cause of
naturally occurring forest fires. Lightning can strike power cables, shrubs, trees, and dry grass, igniting a fire.
According to a BBC database, a total of over 12,000 lightning strikes caused over 650 forest fires across the state of California in August 2020, causing over 1.5 million acres of land to be consumed.
- Volcanoes - Hot lava from volcanic eruptions can flow down mountainsides and start forest fires. Lava's high temperature can burn everything in its path.
- Spontaneous Combustion - Organic materials such as dry leaves or compost can produce heat as they decompose over time. When combined with extreme weather conditions, this decomposition poses a high risk for spontaneous combustion, which can lead to forest fires.
Climate Change And Its Impact On Wildfire Frequency
Climate change is a critical factor that influences the frequency and intensity of forest fires.
Rising global temperatures, prolonged droughts, and changing precipitation patterns have all been found to increase the risk of more wildfires.
Warmer temperatures lead to drier vegetation, while altered weather patterns can extend fire seasons and increase the likelihood of extreme fire events on average.
Addressing climate change is key to mitigating the long-term threat of forest fires and protecting vulnerable ecosystems and communities.
The Impact Of Wildfires
The impact of forest fires is far-reaching, extending beyond the destruction of acres of land and property.
Here are some of the ways that forest fires affect the environment, economy, and public health.
Environmental Consequences
Forest fires have long-lasting effects on ecosystems.
The destruction of vegetation and wildlife habitats caused by fires results in a disruption in the biodiversity of species and ecological balance.
Additionally, wildfires can cause soil erosion, water contamination, and changes in local climate conditions, further impacting the environment.
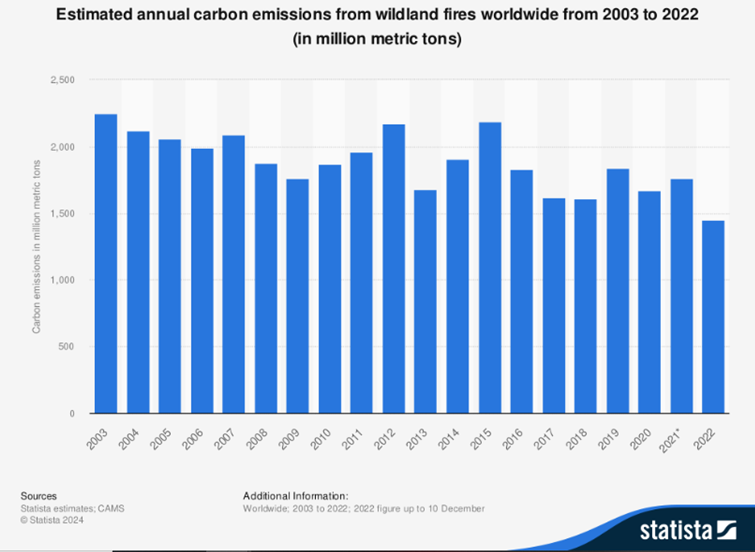
Statistics show that forest fires caused the emission of an estimated 1,455 million metric tons of carbon in 2022.
In the displayed data, forest fires that occurred in 2003 emitted the most volume of carbon with over 2,200 million metric tons.
Effects On Ecosystems And Biodiversity
Data on the increasing carbon dioxide levels coincide with what the world is experiencing today. As temperatures rise, so do ocean acidification and sea levels.
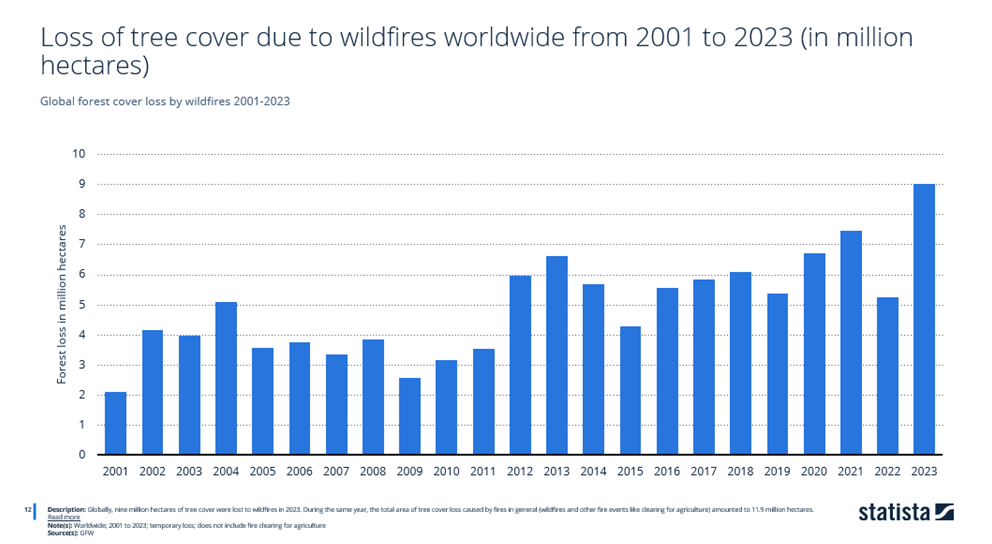
Millions of acres of land are consumed by forest fires, leading to a loss of tree cover, which is essential for the upkeep of ecosystems.
Updated statistics found that 9 million hectares of tree cover were lost to forest fires globally in 2023. In the same year, the total area of tree cover loss caused by all fire events amounted to 11.9 million hectares.
Air Quality Issues
Air quality depreciates as more forest fires occur.
Wildfire smoke contains a mixture of gases and fine particles that can travel long distances, creating haze pollution that can spread up to hundreds of kilometers away from the fire's origin.
This pollution can exacerbate respiratory conditions, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and increase the risk of cardiovascular problems in exposed populations.
Economic Costs
The economic costs of wildfires are substantial and include both immediate expenses and long-term financial impacts.
These costs include the following aspects.
- Property damage
- Firefighting efforts
- Prevention measures
- Economic repercussions for affected communities
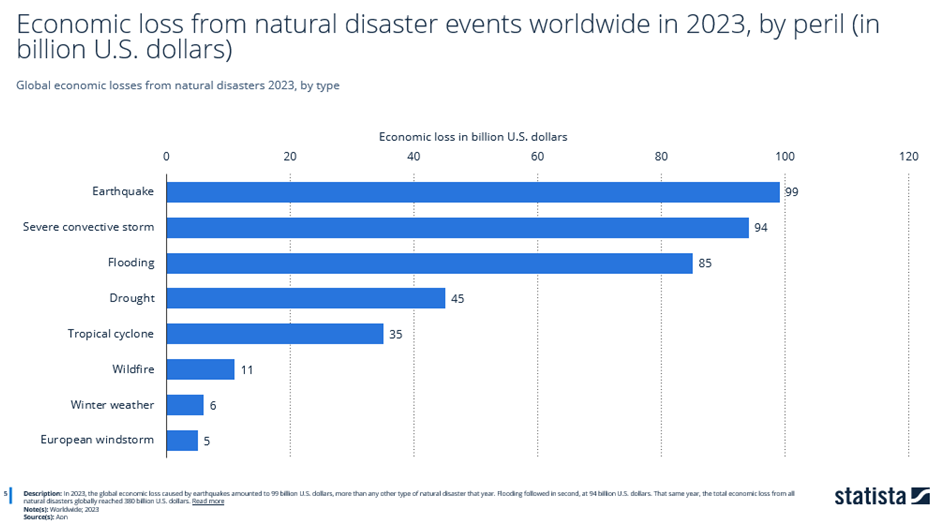
In this figure, statistics shown by the National Interagency Fire Center (NIFC) suggest wildfires contributed to 11 billion U.S. dollars in economic losses worldwide in 2023.
Property Damage Statistics
Forest fires destroy homes, businesses, and infrastructure. The financial toll of forest fires has risen in recent years, often leading to billions of dollars in damages.
These costs include the cost of rebuilding and repairs, plus the economic losses from business interruptions and decreased property values.
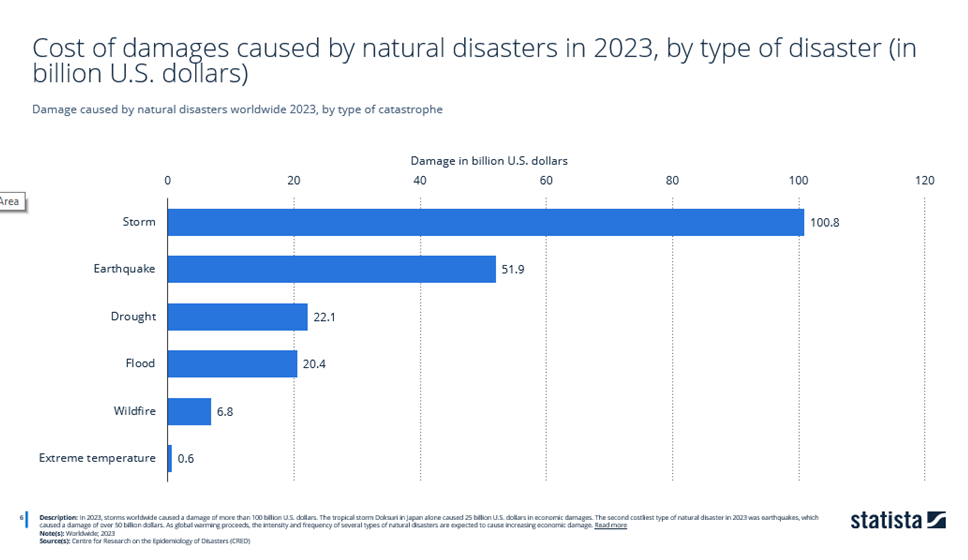
In 2023, wildfires caused 6.8 billion U.S. dollars worth of property damage.
Firefighting And Prevention Expenses
The costs associated with firefighting and wildfire prevention cover the deployment of firefighting personnel, equipment, and resources.
Expenses also include the implementation of preventive measures such as controlled burns, firebreaks, and public education campaigns.
These costs can rise to hundreds of millions or even $1 billion dollars in expenses.
As an example: California, a forest fire-prone state, spent about 1.2 billion U.S. dollars in wildfire suppression in 2022. This expense came a year after the Dixie fire occurred, burning over 963,000 acres across the state.
Human Health And Safety
The immediate dangers of forest fires include burns, smoke inhalation, and injuries sustained during evacuation or firefighting efforts.
Long-term health effects along with the psychological impact can be significant for victims and firefighters alike.
Wildfire-Related Deaths And Injuries
Forest fire unpredictability and the speed at which they can spread make them difficult to respond to.
This leads to fatalities and injuries among residents in affected areas, firefighters, and first responders.
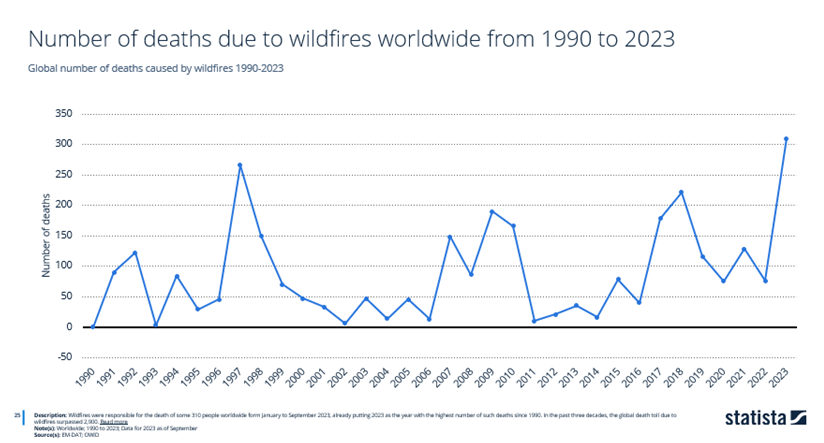
Based on this figure, forest fires caused the death of around 310 people worldwide between January to September 2023.
This makes 2023 the year with the highest number of such deaths to date since 1990. The global death toll for forest fires in the past 30 years has already surpassed 2,900 people.
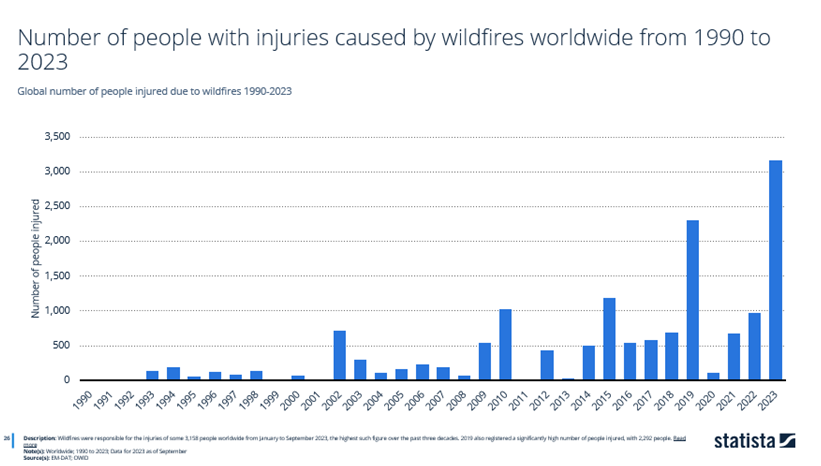
In this figure, forest fires were responsible for the injuries of some 3,158 people worldwide from the date of January to September 2023.
Along with the number of deaths, 2023 is also the year with the highest number of injured victims over the past three decades.
The year 2019 recorded a notably high amount of injuries, with 2,292 people being injured.
Long-Term Health Effects
Exposure to wildfire smoke has been linked to chronic respiratory and cardiovascular conditions.
On the other hand, the stress and trauma of experiencing forest fires can lead to lasting mental health issues, such as the following.
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Wildfire Management And Prevention
Wildfire management and prevention involves an analysis of the statistics and current strategies to develop more effective initiatives.
These may include innovative technologies, and awareness efforts that aim to reduce the frequency and impact of wildfires.
Current Strategies And Their Effectiveness
Current wildfire management strategies focus on a range of preventive and responsive actions. These include:
- Prescribed Burns - These are controlled fires intentionally set under precise conditions to reduce fuel loads. They are highly effective at preventing larger fires by eliminating excess vegetation.
- Firebreaks - Firebreaks are strips of land that are cleared of vegetation to act as barriers, slowing the spread of wildfires. These provide safe zones for firefighters.
- Forest Management Practices - Some examples include the thinning, pruning, and removing of dead trees to maintain healthy forests and reduce fire risk. This long-term strategy helps reduce the amount of flammable material that may further fuel a fire.
- Rapid Response System - This system helps deploy firefighting assets and personnel to newly detected wildfires to contain them before they spread. This is crucial to minimize damage and prevent fires from growing.
- Vegetation Management - The regular clearing of brush, grasses, and other flammable materials in high-risk locations will reduce fuel loads and slow down fire spread. Consistent clearing efforts are necessary to be effective.
Technological Advancements In Wildfire Detection
Satellite imagery and remote sensing technologies provide real-time monitoring of wildfire activity, enabling early detection and rapid response.
Here are a few notable technological advancements for wildfire detection:
- Fire Urgency Estimator in Geosynchronous Orbit (FUEGO) - Although still in the concept stage, FUEGO is a series of drones and satellites equipped with infrared sensors that hope to detect early signs of forest fires from space.
- Drones - These machines help monitor wildfire spread when the smoke is too thick for manned aircraft.
- Thermal Imaging/ Infrared Cameras - These can detect and report heat from forests even without a flame.
- I4F Instant Foam - This foam technology accurately coats forest areas and extinguishes fires more efficiently than water.
- Firefighting Robots - These remote-controlled robots come equipped with a firefighting nozzle, blade, and winch.
- AI-supported Sensor Networks - Networks can provide real-time data on high-risk locations so that firefighters and first responders can access up-to-date information and facts regarding fire location, intensity, and direction.
Community Preparedness And Education Initiatives
Community preparedness and education initiatives require collaboration between government agencies, local organizations, and community members.
Every community should initiate the following:
- Public Awareness Campaigns - Educate residents about fire safety practices, such as creating defensible spaces around their homes and adhering to fire bans during high-risk periods.
- Community Drills and Evacuation Plans - Ensure that residents are prepared to respond quickly and safely during wildfires.
It is important to be ready for a wildfire long before it happens. Homeowners should consider
ignition-resistant homes, having emergency supplies available, and planning escape routes.
Damaged Home? Get a Fair Price Today
Not all buyers are interested in fire-damaged home, but we can help find someone who is. Request a cash offer from Fire Cash Buyer's extensive investor network and work with one of our home consultants to move forward.
Long-Term Trends And Predictions
Facts and trends can help concerned individuals make informed predictions for future wildfire scenarios.
Historical Wildfire Data Analysis
Analyzing historical wildfire data provides valuable insights into the patterns that have shaped wildfire activity over time.
Data analysis reveals how factors such as climate variability, land use changes, and human activities have influenced the number of fires that occur and the acres they burn in a given location.
Furthermore, data analysis helps with:
- Early detection and proper resource allocation during wildfires
- Insurance and risk assessment in fire-risk locations
- Supply chain management
Future Projections Based On Climate Models
Climate models suggest that rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and changing precipitation patterns will create conditions more conducive to wildfires.
Regions that traditionally experience moderate fire activity may see increased wildfire risks. In addition, already vulnerable locations may face more frequent and severe fires.
These projections emphasize the need for adaptive management strategies and increased investment in wildfire prevention and response capabilities.
Potential Shifts In Wildfire Patterns And Intensity
As climate change continues, wildfire patterns may change, resulting in longer fire seasons, increased fire intensity, and the potential for a larger acreage at risk.
Additionally, changes in vegetation types and distribution due to climate change could lead to new fire events, requiring close monitoring and adaptation to manage these threats.
Global Perspective On Wildfires
This section will compare U.S. wildfire statistics to other countries. This data should provide an indication of the importance of international collaboration in wildfire research and management.
Comparison Of U.S. Wildfire Statistics To Other Countries
The United States is not alone in facing the challenges posed by forest fires. Brazil, Mediterranean nations, Australia, and Canada also experience significant wildland fire activity.
When comparing U.S. wildfire statistics to these regions, several key differences and similarities emerge.
For instance, Australia experiences severe bushfires, particularly during its hot and dry summer months just like the ones in the state of California. Canada, on the other hand, experiences fires primarily in its vast boreal forests.
South America
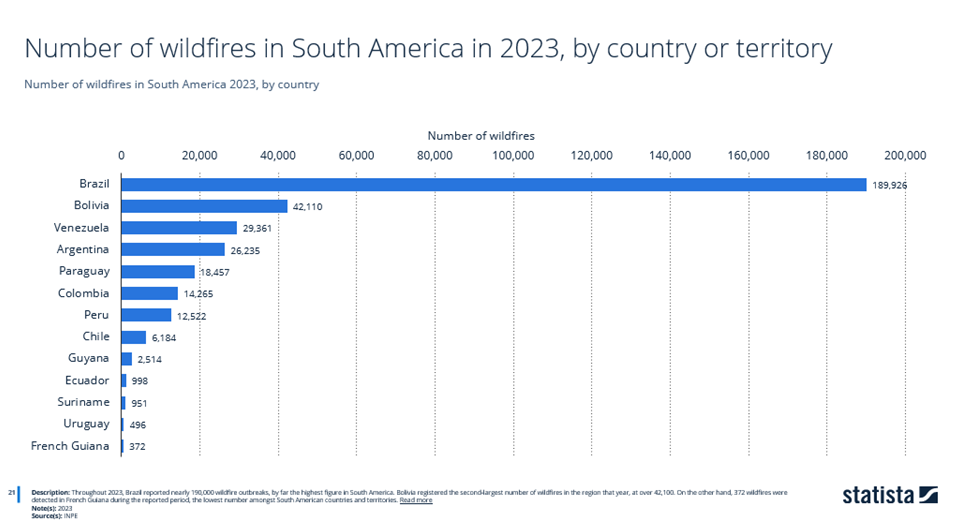
Statistics for forest fires in South America show a large figure for Brazil alone, with almost 190,000 outbreaks throughout 2023.
According to the database, this is the highest figure in South America to date. Bolivia recorded the second-largest number of forest fires in the region that year, at over 42,100.
As Brazil climbs to be the leading producer of soybean and beef worldwide, more acres of land are reallocated for farming purposes, reducing the amount of available forest cover.
The forest fires in the country are further exacerbated by deforestation and industrial agriculture.
The Mediterranean
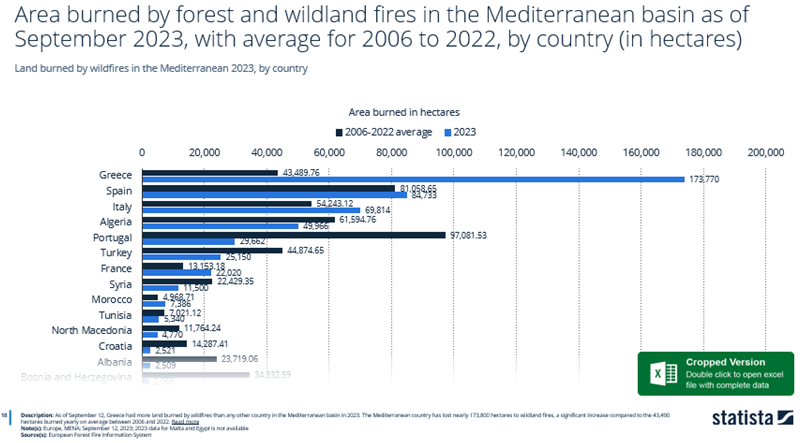
As of September 2023, Greece had the largest area burned by forest fires compared to any other country in the Mediterranean basin.
Based on this database, Mediterranean countries lost nearly 173,800 hectares to wildland fires in 2023.
This is a significant increase compared to historical records, which display an average of 43,490 hectares of area burned between 2006 and 2022.
Canada
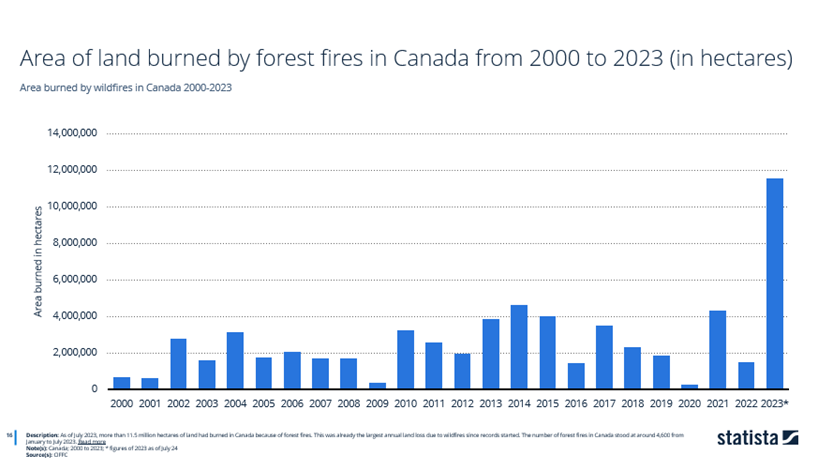
As of July 2023's database, more than 11.5 million hectares of land burned in Canada due to forest fires, marking the largest recorded figure to date.
In addition, the number of forest fires that occurred in Canada was around 4,600 from January to July 2023.
International Collaboration In Wildfire Research And Management
International collaborative efforts include joint research initiatives, data sharing, and coordinated response strategies to improve global wildfire management capabilities.
An International Wildland Fire Summit is occasionally held for participating nations to develop short and medium-term solutions to the threat of forest fires worldwide.
The United Nations also has several agencies and programs established to help in mitigating the impact of forest fires, such as the following.
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) - FAO helps countries move toward sustainable forest management along with fire management, and community involvement.
- Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) - OCHA aids in the coordination of international response to wildland fire emergencies.
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
- This agency creates an environmental impact assessment of vegetation fires and helps with early warning and monitoring.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many acres were burned and how many wildfires occurred in Texas and California in 2024?
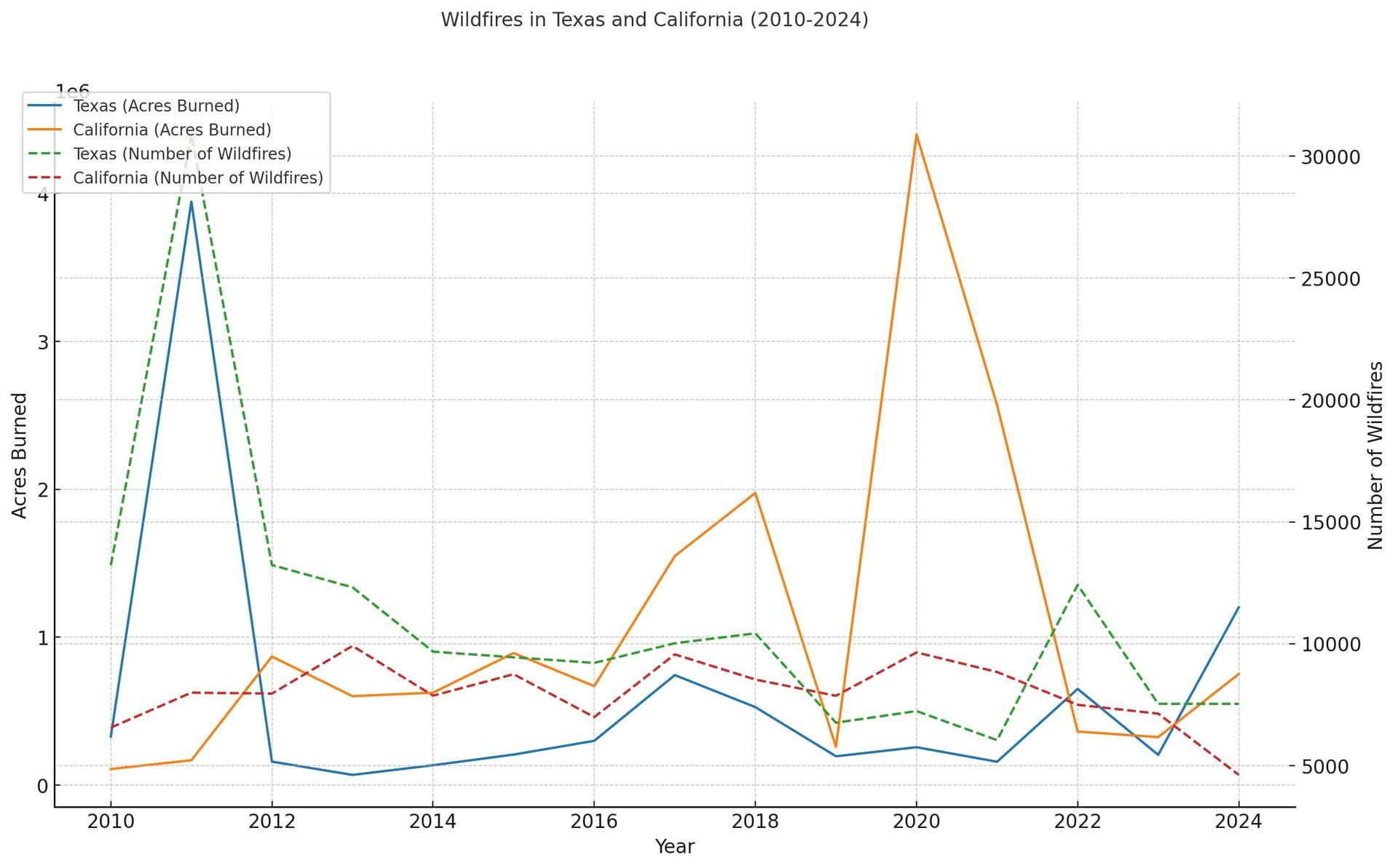
In 2024, Texas experienced 1,202,617 acres burned and 7,530 wildfires. California saw 751,327 acres burned and 4,613 wildfires.
What are the predicted trends for wildfires in the United States for 2025 and 2026 based on the provided data?
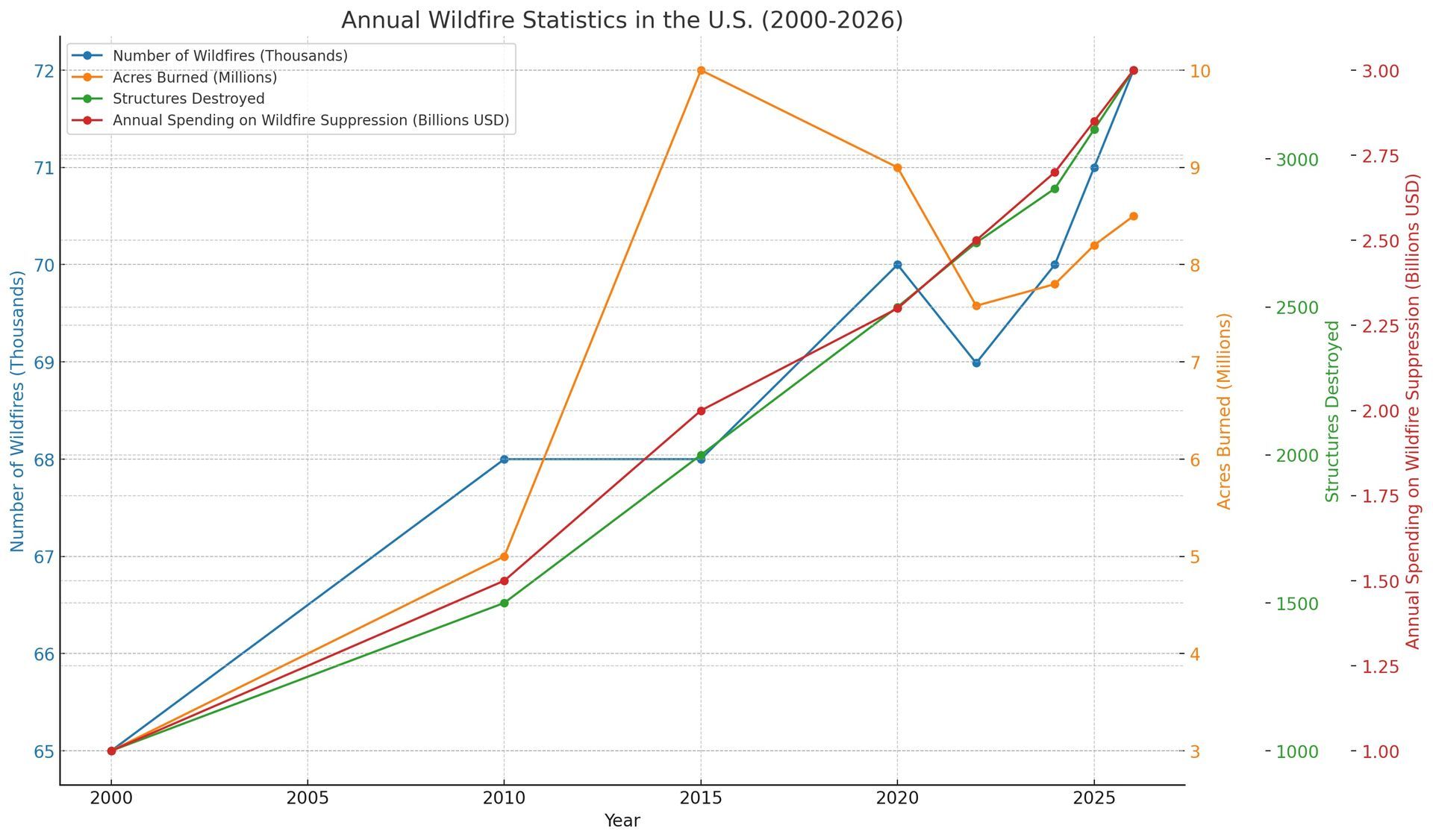
The provided data indicates several key trends for wildfires in the United States for 2025 and 2026:
1. Number of Wildfires: The number of wildfires is projected to slightly decrease from approximately 72,000 in 2025 to around 71,000 in 2026.
2. Acres Burned: The area burned by wildfires is expected to rise significantly, reaching 10 million acres in 2025 before stabilizing at around 9 million acres in 2026.
3. Structures Destroyed: The number of structures destroyed by wildfires is anticipated to increase to about 3,000 in 2025, followed by a slight decrease to around 2,500 in 2026.
4. Annual Spending on Wildfire Suppression: The spending on wildfire suppression is expected to continue its upward trend, reaching approximately $2.75 billion in 2025 and surpassing $3 billion in 2026.
These predictions suggest that while the number of wildfires might slightly decrease, the severity and financial impact of wildfires will likely continue to grow in the upcoming years.
How Many Wildfires Occur in the United States Each Year?
The number of forest fires that occur each year varies. In the most recent statistics, the United States experienced 55,571 wildfires in 2023. The measure of these fire incidents relies on the number of acres burned and the overall impact.
What Percentage of Wildfires Are Caused by Humans?
Approximately 85-90% of wildfires in the United States are caused by human activities. These include fires caused by unattended campfires, discarded cigarette butts, malfunctioning equipment, and other preventable actions.
How Much Does Wildfire Suppression Cost Annually?
To fight wildfires, every state must spend a few million to billion dollars per year on wildfire suppression costs.
These expenses cover the following.
- Firefighting efforts
- Resource deployment
- Other immediate actions to control and extinguish wildfires
For example, California spent 1.2 billion U.S. dollars on fire suppression expenditures in the fiscal year ending June 2022.
Are Wildfires Becoming More Frequent and Severe?
Yes. Climate change, prolonged droughts, and increased human activity in fire-prone locations contribute to the rising incidence, number of acres burned, and intensity of wildfires.
What Can Individuals Do to Prevent Wildfires?
Individuals can take the following steps to prevent wildfires.
- Following local fire regulations and restrictions.
- Creating defensible space around homes by clearing flammable vegetation.
- Properly extinguishing campfires and disposing of smoking materials.
- Staying informed about fire weather conditions and avoiding activities that could ignite fires during high-risk seasons.
💡 Conclusion
By analyzing wildfire statistics and data, we can better understand the growing threat of wildfires and develop effective strategies to mitigate their impact.
Through continued research, technological advancements, and public education, we can work towards reducing the frequency and severity of wildfires, ultimately protecting our environment, economy, and public health.
By staying informed of the latest wildfire statistics and raising awareness of the latest mitigation tactics, citizens can help prevent the spread of future wildfires.